Cyberattack 2024 Insights: The Threat Landscape and How to Secure Your Organization
 It’s already been a busy year for cyberattacks. From increasingly large data breaches to AI vulnerabilities, staying informed about the cyberattack 2024 trends is essential to preventing a costly and embarrassing breach. The recent National Public Data Breach exposed 2.7 billion records from an identity verification company. These records were unencrypted and reportedly contained names, social security numbers, and decades worth of personal addresses. This information is often enough to get you full access to someone’s credit report account!
It’s already been a busy year for cyberattacks. From increasingly large data breaches to AI vulnerabilities, staying informed about the cyberattack 2024 trends is essential to preventing a costly and embarrassing breach. The recent National Public Data Breach exposed 2.7 billion records from an identity verification company. These records were unencrypted and reportedly contained names, social security numbers, and decades worth of personal addresses. This information is often enough to get you full access to someone’s credit report account!
To help you combat today’s latest attacks, our team has analyzed and compiled an overview of new, significant attack trends, including the most interesting hacks from Black Hat and DEFCON, as well as actionable advice to mitigate these risks. Without further ado, let’s dive into the latest cyberattack 2024 trends!
The 5 Latest Cyberattack 2024 Trends, Threats, and Proactive Prevention Advice
- AI’s Cybersecurity Risks
As AI continues to integrate into everyday applications, the cyberattack 2024 landscape has seen a surge in threats related to AI vulnerabilities. Richard Haran, a security architect at Nvidia, outlined several concerns, including plugin vulnerabilities that enable remote code execution, SQL injections, and prompt injection attacks that manipulate AI models like ChatGPT.
Key AI Cyberattack 2024 Trends:
-
- Plugin Vulnerabilities. Weak points in AI plugins can be exploited for remote code execution, SSRP, SQL injection attacks, and more.
- Indirect Prompt Injection. Attackers manipulate AI prompts, bypassing ethics guardrails to access sensitive data or generate harmful code. One example is “Typoglycemia” where attackers leave out the vowels in commands to trick AI models into providing dangerous outputs.
- Insecure Permissions and Boundaries. Poorly configured AI systems can leak data, leading to significant security breaches.
- Exploiting AI Programs. Michael Barguey, the CTO at Zenity, gave a fascinating presentation on 15 ways you can break your Microsoft AI Copilot program. Here are a few examples:
- Prompt injection. Hackers alter AI prompts to reveal data (even conversations between employees) or perform harmful actions. For example, a hacker who gains access to Copilot can use a malicious prompt asking Copilot to recap previous prompts.
- Remote code execution. Attackers who gain access and control of Copilot can manipulate data and systems, i.e. using the system to execute malware code.
- Data theft. A vulnerability can be exploited to extract sensitive, inside information that employees have entered into the AI.
- AI corruption. Attackers can tamper with AI logic and alter the AI to provide malicious information to the users. It becomes an insider threat.
Mitigating AI-Related Cybersecurity Threats:
-
- Harden AI Implementations: Regularly review security settings, update configurations, and enforce strict privacy policies.
- Monitor AI Usage Across All Software: For instance, Google’s Gemini AI was installed on users’ phones without consent, reading texts and other data immediately after installation—highlighting a significant data privacy concern.
- Implement Strict Use Policies: Clearly define how AI tools can be used within your organization to prevent unauthorized actions.
- Third-Party Software Risks

Delta was one of many airlines that had to cancel their flights. You can see the “Blue Screen of Death” on the right.
The CrowdStrike update outage of 2024 highlighted the risks associated with third-party software updates and patching. The update caused widespread system failures, “bricking” computers around the world and halting operations for many organizations. Compounded by the use of BitLocker (which is a best practice but requires a different key for every computer and individual restoration), which prevented systems from booting into safe mode, this event demonstrated the importance of having robust Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) policies and strong Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) plans.
Lessons Learned from the CrowdStrike Incident:
-
- Maintain Secure Access to Critical Recovery Information. Ensure BitLocker keys and your critical passwords are stored in a secure yet accessible location.
- Consider Patching Timeframes. Weigh the risks of immediate patching (which can prevent a zero-day attack) against the benefits of delaying updates by 8 hours to detect issues.
- Sandbox Updates Before Deployment. Test new updates in a controlled environment to catch potential issues before they impact your entire network.
- Develop a BCDR Plan for Failed Patches. Ensure your Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) plan accounts for the possibility of patch failures.
- Be Aware of Phishing Attacks Post-Outage: After large-scale incidents like this, phishing attacks pretending to have information on the outage often spike as attackers seek to exploit the chaos and anxiety. Be vigilant for phishing emails spoofing well-known companies like CrowdStrike.
- Cloud Misconfiguration Attacks
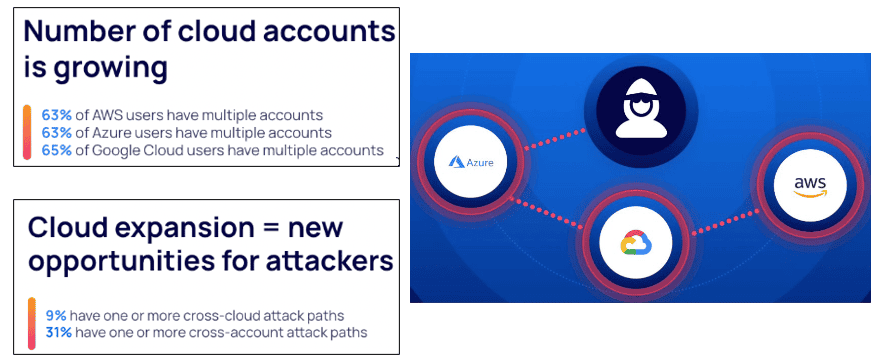
Increased cloud use yields new opportunities for attackers.
Cloud misconfigurations remain a leading cause of security breaches in the cyberattack 2024 landscape. According to a recent survey, 63% of major cloud users have multiple accounts, and 40% have either cross-cloud or cross-account attack paths, making it easy for attackers to jump between cloud platforms once they gain access.
Reducing Your Risk from Cloud Misconfiguration Attacks:
-
- Adopt Multi-Cloud Security Solutions. Use centralized security tools to manage and assess risk across all cloud environments.
- Enforce Least-Privilege Access. Limit permissions to reduce the risk of cross-account and cross-cloud attacks.
- Prioritize the Protection of Critical Assets. Secure essential business data, such as customer information, intellectual property, and financial records, and closely monitor access. Ensure you know where sensitive data is stored and who has access to this information.
- Conduct Regular Cloud Configuration Reviews and Pentests. IT teams regularly spin up new cloud services and it’s easy to make an error. Have regular configuration reviews and pentests of your cloud environments.
- Breaching AWS Accounts Through Shadow Resources
Aqua Security’s presentation on breaching AWS accounts through shadow resources highlighted how automatically created AWS assets, often unnoticed by users, can be exploited when hackers can guess the predictable naming pattern. For example, predictable naming patterns in AWS CloudFormation can lead to S3 namesquatting attacks, where attackers guess and hijack resources before legitimate users deploy them. For further details on this type of attack, watch our Summer Hacking Trends video.
Protecting Against AWS Shadow Resource Exploits:
-
- Use Unique Naming Conventions. Avoid predictable names for S3 buckets so hackers can’t guess the names of your buckets.
- Apply Strict Identity and Access Management (IAM) Policies. Enforce tight access controls to limit who can access and modify your resources.
- Monitor with AWS CloudTrail and Access Logs. Track unauthorized access and respond swiftly.
- Conduct Regular Audits. Regularly audit your cloud environment to detect and remediate shadow resources and misconfigurations.
- The Classic Data Breach
Last, but not least, classic data breaches with extortion attacks or ransomware attacks are still big business for criminals. Let’s look at some of the biggest data breaches of 2024:
-
- National Public Data:7 billion records
- Ticketmaster: 560 million records (this breach stemmed from the third-party Snowflake breach—which compromised around 165 Snowflake customers)
- AT&T: Nearly 110 million people impacted
- Change Healthcare: Estimated to have impacted half of US citizens and shut down many medical offices for days.
Protecting Against Massive Data Breaches:
-
- Implement Zero Trust Security Models: Limit access to data and resources to only those who absolutely need it.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Use strong encryption methods to protect personal information, both in transit and at rest.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Routine penetration testing and security audits can help identify vulnerabilities and gaps in your security infrastructure.
We hope these cyberattack 2024 trends and prevention tips are helpful! Please contact us if you need help with technical testing, advisory and policy development services, cybersecurity solutions, or training. Our expert team is ready to assist you!
