Cybersecurity Budget Tips that Deliver the Most Bang for Your Buck

Cybersecurity Budget Trends
Cybercrime continues to increase. The FBI’s Internet Crime Report shared that there was a record-breaking 847,376 complaints with potential losses of more than $6.9 billion in 2021. So, it’s no surprise that cybersecurity spending is up to combat these increasing attacks. McKinsey and Company estimate a 15% annual increase in costs related to cybercrime through 2025, and their data indicates that 85% of small and midsize enterprises intend to increase their IT security spending through 2023.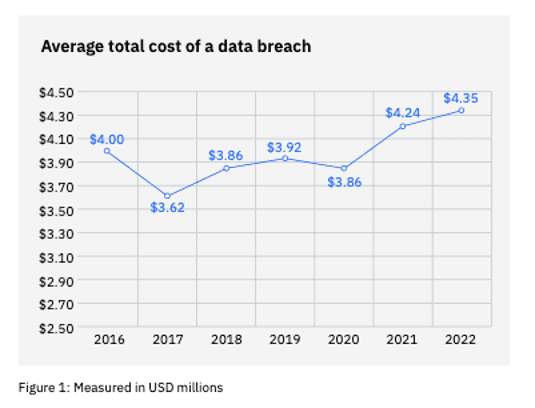
Why are these organizations spending so much more on cybersecurity? Both the number of internet crimes and the damages resulting from these cybercrimes has increased. IBM found that the average worldwide total cost of a data breach was $4.35 million USD, with the average US cost of a breach reaching a staggering $9.4 million USD—the highest in the world. The damage is not just direct cash losses, organizations also face public backlash, potential compliance or regulatory fines, loss of customers and prospects, and more. It’s easy to see why smart executive teams seek to limit the risk of a data breach by increasing their cybersecurity spending.
The next question that most organizations ask is how much they should allocate to their cybersecurity budget to reduce their risk. While there’s no one size fits all answer to this question, here are three key factors to consider:
- What is your risk? Compare your current cybersecurity gaps with today’s emerging threats or get a risk assessment to help you understand your risks. Make sure you’re also aware of your compliance and contractual cybersecurity requirements for your customers, cyber insurers and partners. At a minimum, you will want to ensure your organization has solutions in place to meet all contractual or compliance obligations. Check out LMG Security’s YouTube channel for regular updates on cybersecurity threats and trends.
- What is your organization’s risk appetite? Once you have analyzed your risks, your organization needs to decide how to treat each risk – the standard options are to avoid, transfer, mitigate or accept each risk. For more information, read this blog that explains the standard risk treatment options and offers strategies on how to prioritize your risks. Make sure your residual risk is aligned with your leadership’s expectations.
- How much do you need to spend to get your risk level to a point where your organization is comfortable? This is your budget – or allocate as much as you can and have a plan for adding more security controls next year.
Think of cybersecurity as a journey, not a destination. The goal is to improve your cybersecurity as much as you can each year and have a multi-year plan that continually minimizes your risks.
How to Prioritize your 2023 Cybersecurity Spending
If you remember our blog on Creating an Effective Cybersecurity Plan, there are four crucial elements:
- Know what you’re trying to protect
- Understand your obligations
- Monitor your risk
- Manage your risk
The good news is that risk management isn’t just about how much you spend—it’s also about smart spending decisions. Let’s get down to the nitty-gritty; here are the foundational cybersecurity budget items that we feel deliver the most bang for your buck.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is critical in today’s threat landscape, where criminals routinely break into cloud login forms and remote desktop interfaces. Essentially, it is an added layer of protection to verify it’s really you who is accessing your account and not a hacker. It’s one of the simplest, most cost-effective strategies organizations can use to reduce risk in a variety of areas. (In fact, two very popular MFA options are free!) You should enable MFA on every internet-facing account and device possible. However, not all MFA is equally effective. For example, text message (SMS) MFA is much less secure than smartphone apps or hardware tokens. In addition, try not to use email as a backup authentication method. If criminals are already in your email, they can use the email backup to capture your authentication code. Many organizations now use authenticator apps, issue hardware fobs such as the Yubikey for authenticating employees or set up biometric authentication using fingerprints or facial recognition. However, any type of MFA is better than no MFA. You can outsource a managed MFA implementation service or do it yourself with free MFA implementation videos that provide step-by-step instructions for deploying popular MFA services from Microsoft 365, G-Suite, and Duo (that supports SSO and has advanced management capabilities). If you are looking for best practices and advice on what solution is best for your organization, read this MFA tip sheet.
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR) & extended detection and response (XDR). EDR is a more robust endpoint security solution that is a step up from traditional signature-based antivirus. Leading EDR tools offer a robust integrated threat intelligence solution with continuous real-time monitoring and behavioral detection as well as immediate mitigation and response, threat hunting, and historical forensic data collection capabilities. EDR lets you quickly investigate and respond to incidents in a way that antivirus cannot. With EDR, the solution not only detects and immediately quarantines threats, but it also provides the information you need for threat hunting and includes response capabilities. To learn more about EDR, watch this 6-minute EDR video). XDR further extends the capabilities or EDR and incorporates different data sources from your network, email, and cloud, as well as integrates with SIEM and SOAR systems. When it comes to your cybersecurity budget, IBM’s report says that XDR can cut 29 days off your time to contain a breach, and as many studies have proven, faster breach containment lowers your costs from a data breach.
- On-demand employee cybersecurity awareness training. The 2022 Verizon Data Breach Investigation Report found that 82% of breaches involved a human element – e.g. social engineering – and over 60% of those attacks were a result of phishing. Training is crucial to turn everyone in your organization into part of your first line of defense against cyberattacks. If you can train your employees to spot a phishing attempt and report it, you can dramatically reduce your risk of a data breach. It’s important to routinely communicate cybersecurity policies, procedures, and best practices to all internal stakeholders, including IT staff, security team members, legal counsel, general employees, and the leadership team. But the most effective path is to provide general cybersecurity awareness training for every employee in your organization by subscribing to a security awareness training portal. This provides monthly lessons and quizzes for all employees, and many have phishing simulation tests. Whichever solution you choose, ensure the training stays current and addresses the latest threats like MFA bypass and MFA fatigue attacks. This security strategy delivers a solid ROI. One recent study found that a strong employee training programs reduced breach costs by $247,758. If you still can’t find room for this training in your cybersecurity budget, download free tip sheets and email them directly to your employees about phishing prevention, password security and remote work safety. Then cover new topics each month in an employee meeting. Don’t forget there are also other groups in your organization that needs specialized training, such as your cybersecurity responders and executive board.
- Continuous attack surface monitoring. Today’s cybercriminals are constantly scanning the Internet for vulnerable systems, and all too often, they find them. Zero-day vulnerabilities like Log4j are on the rise, especially since cybercriminals have stolen the source code for many key software suites. This enables them to comb software for vulnerabilities and write new exploits which they sell to other criminals on the dark web. Now that the market for exploits is mature, expect to see zero-day vulnerabilities continue to emerge regularly. To protect your organization, use continuous attack surface monitoring to scan your Internet-facing perimeter for vulnerable systems, and make sure you act on the alerts.
- Patch management tools. Implementing strong software patch management policies are crucial to counter zero-day vulnerabilities. According to a survey conducted by the Ponemon Institute, 42% of the respondents that had been breached stated that the cause was a known, unpatched vulnerability for which a patch was available but not applied. Many organizations have a patch management policy that calls for monthly or bimonthly patching cycles. But when a critical vulnerability is announced, hackers may actively try to exploit your server within hours or days, not weeks. You need to update your patch management policies and procedures to ensure quicker patching for critical vulnerabilities and ensure strong patch verification. Consider using an automated patch management cybersecurity tool or a continuous vulnerability management solution. This will enable you to catch the systems that are out of date for patches. Don’t forget to verify that patching was successful. Many organizations think they have successfully patched their software, only to find out later the patch failed. Finally, you need to inventory all of your operating systems and third-party apps, so you know which patches you need to apply. Read this blog on software patch management tips for more information.
- AI and automation. According to IBM, organizations that incorporate AI and automation into their cybersecurity suite reduced the average cost of a breach by close to 50%. Organizations with fully deployed security automation had an average breach cost on $3.15 million, versus an average cost of $6.2 million for organizations without fully deployed security automation. In addition to reducing costs from a breach, offloading time-sensitive, manual, or repetitive work to AI and machine learning solutions saves time and employee hours, as well as helps to proactively reduce the risk of a breach. The same IBM study found that organizations found and contained a breach 27% faster when using AI and automation. AI is ever vigilant; it can be incorporated into proactive and reactive tools to detect and stop the spread of malware or attacks in minutes. For example, if you incorporate the Mimecast X1 AI-enhanced phishing and malicious email prevention tool, the AI capabilities incorporate social graphing that reviews application usage, activity data, and location, to identify anomalous behavior in real-time. It automatically looks for malicious patterns, attachments, URLs and even checks odd phrasing of email content to detect and block phishing attacks. Furthermore, it uses a mesh system that integrates with common security vendors, so you get a better idea of where suspicious activity originates.
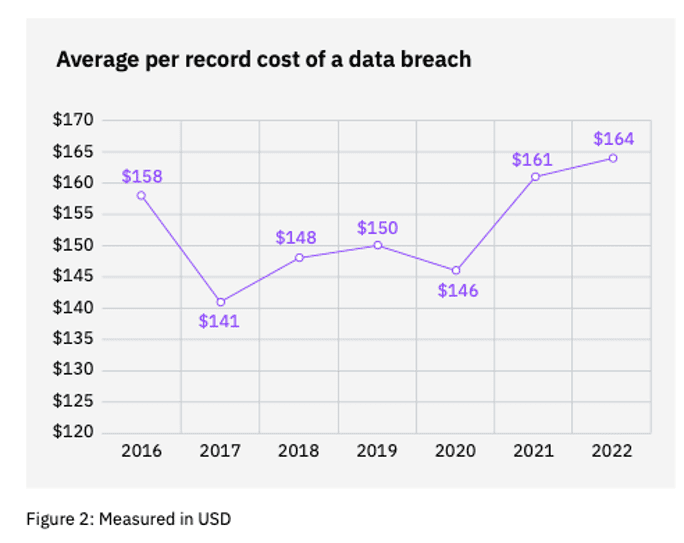
- Data retention and backups. Data is hazardous material. Reducing the amount of data you hold is one of the cheapest and most effective ways of reducing your risk. The IBM report found that the average cost per record in a data breach was $164 in 2022.
- Zero trust. The reality is that even with great cybersecurity, your organizations can still get hacked. If you are breached, having a zero-trust environment reduces access and privileges so you can minimize the damage. There are several different approaches to zero trust that can be a substantial time commitment for your organization. One of the lighter and less expensive options is to incorporate technology such as Secure Auth that for about $1 per user, requires continuous verification throughout your environment.
- Invest in skilled staff. Hiring cybersecurity staff continued to be a major challenge for organizations. A recent survey found that 62% of organizations say they do not have enough cybersecurity staff. So how can you make the most of your cybersecurity budget?
-
- Invest in internal training. Some training materials are even free. If you use AWS or Azure, both offer free, online training materials that are fairly comprehensive. Allocate hours each month for employees to do continuous training on everything from your cloud environment and programs to incident response.
- Every organization needs an experienced CISO or security leader. IBM found that having a skilled CISO decreased the average cost of a breach by $144,915. But skilled CISOs are hard to find and expensive to hire. Unless you are a large enterprise organization, you can save money, get the skilled leadership you need, and meet cyber insurance and compliance requirements with a fractional CISO.
- It pays to outsource some cybersecurity specialty skills. Don’t struggle with policy development or implement unfamiliar solutions if that is not in your team’s skillset. You can bring in outside experts to augment your staff if you need a particular skill or additional staff for a project. These specialists have likely seen this scenario before and will be able to handle it faster and more effectively, which is great for your cybersecurity budget bottom-line.
We hope these suggestions and data points help you determine the budget and risk reduction strategies that are right for your organization. If you need additional help analyzing your risks or implementing many of the services in this blog, you can contact the LMG Security team for help. Let’s all Achieve Nothing in 2023!
