How the Dark Web Works

How the Dark Web Works 101
We’re going to start with a warning. The dark web is not safe. Just browsing to a site can infect your device with some pretty nasty malware, so proceed with caution or better yet, don’t browse the dark web at all. When security researchers browse, we do so from sandboxed computers to protect our network. Now, on to the basics.
The dark web is popular with criminals because it provides anonymity. It is built on top of the regular internet, uses different browsers (the most popular is Tor), and requires custom protocols and software to access sites using various security protocols. On a normal website, your traffic goes to a web server. On the dark web, you go through multiple intermediary computers (frequently 3-5) before reaching your destination. By using security protocols while making these connections, it makes it impossible for others to track your actions.
The most popular protocol, onion routing, ensures anonymity because the source and destination cannot be seen, and messages are encrypted in layers (like an onion). Each node peels off the outer layer and exposes the next address of the next destination. It encrypts the routing data to ensure no one can see your entire path—this is what provides anonymity. We won’t go into encryption here, but you can learn more in these videos: How Encryption Works and How the Dark Web Works.
How do you reach a site on the dark web using the Tor browser? You travel a “circuit,” which is a path through the network that consists of a:
- Guard node: Node “A” below is the entrance computer that is a trusted source and must be authorized
- Middle node: Node “B” below is a node that can’t talk directly to the source or destination
- Exit node: Node “C” is the last stop before your destination
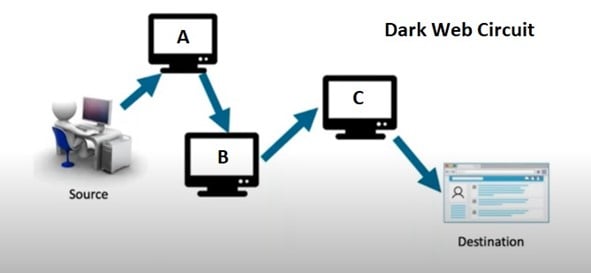
The image above shows you an example of a dark web circuit and how it goes through multiple computers to get to the destination.
If you’re browsing, you can’t tell who is running the site you’re visiting and vice versa. As we mentioned, anonymity is the foundation of how the dark web works. This way, the FBI cannot map your computer to the website you are visiting—a clear benefit for cybercriminals.
Does this mean the dark web is private? NO. Onion routing software is designed to preserve anonymity, not confidentiality. While you can add additional encryption software such as TLS and PGP, it’s not always included by default. If the content is not encrypted, any information you enter, or specific hardware fingerprints could be captured if a node is compromise and someone is watching. Most famously, Julian Assange founded WikiLeaks by sourcing massive streams of information that he gathered by monitoring traffic on a dark web exit node.
How Do You Get to the Dark Web?
Many Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), Reddit, and Reddit’s evil cousin Dread (which is more of a criminal forum), all have listings of popular sites on the dark web. If you use Tor to access the dark web, many the addresses will look very different and end in “.onion”.
What Can You See on the Dark Web?
You can visit “normal” websites (also called “clear web” sites) like Google.com, but it may run slower with each different computer you are routed through, and pages may be in a different language since you can’t predict the countries through which your traffic will travel. One of the key differences between how the dark web works and how the normal a.k.a. clear web works, is that the dark web is more difficult to navigate. To find sites on the dark web, many people use a site that serves as a directory or “search engine,” such as the Hidden Wiki. There are also other “search engines” like Haystack, Torch, and Recon, but these sites are all incomplete since it is not possible to “crawl” every site on the dark web, and addresses change often (as frequently as every few days or hours). So, while these guide sites are essential to finding your destination, you should be very cautious.
What are some of the popular destinations?
- Dark web markets: You can buy a wide variety of illegal items such as social security and credit card numbers, drugs, vaccines, medical profiles, full personal data profiles, and much more.
- Hacking group blogs and websites: You can see the blogs from hacking groups, exposure extortion sites that are publishing data when organizations don’t pay a ransom, advertisements that offer big money for access to target networks, and more.
- Regular clear web sites: There are a number of legal reasons people use the dark web to access clear web sites. Some people want to browse anonymously or exfiltrate information without leaving a trail (such as a whistle blower).
An Inside Peek at Dark Web Marketplaces
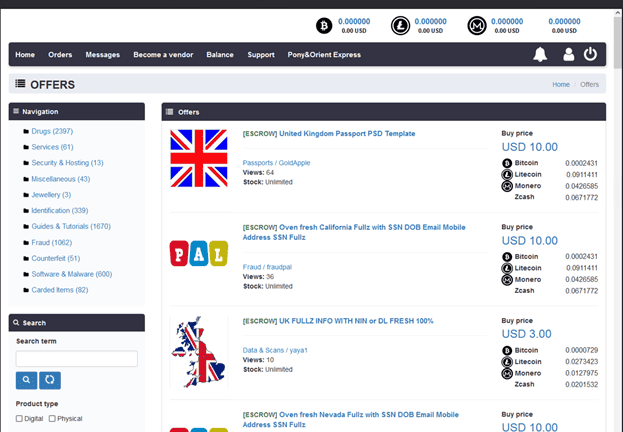
All this information is well and good, but we bet you’d like to take a peek at the dark web. So, let’s dive right in! Our first stop is the Kingdom marketplace. Below is a screenshot of fresh full data profiles and EK passport templates with prices ranging from $3 – $10.
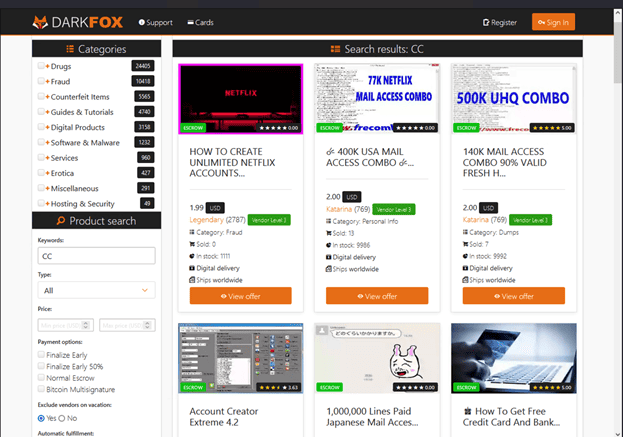
Our next stop is the DarkFox marketplace with images of email addresses, account creation tools, and hacking advice for sale.
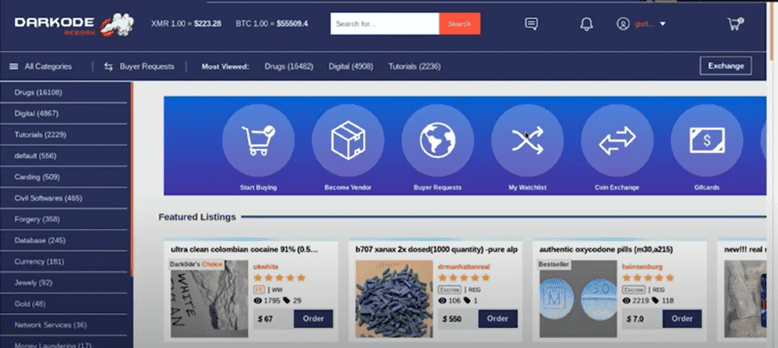
Our final stop is the DarkOde marketplace. In this screenshot you see listings for drugs rather than stolen information. You may notice that all three of these sites looks quite similar to a regular clear web ecommerce site, just with illegal products. There are advanced search features, notifications, and customer service buttons, which make it easy for the criminal community to shop the markets.
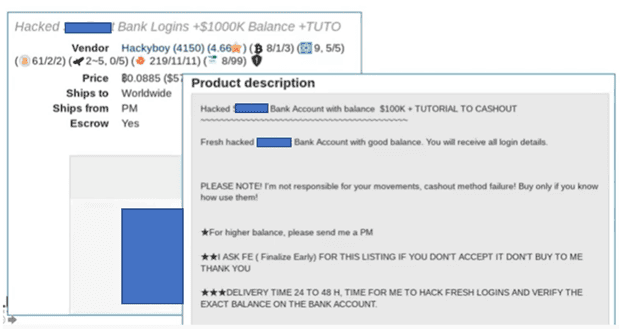
To give you visibility into the listings themselves, we have an example of the additional information you can find once you click on a listing. In the next image below, you can see an ad on another site selling bulk bank logins. These sample images don’t capture the full range of products available in dark web marketplaces. Criminals also sell hacking tools, access information, and even offer their services—complete with their hacking resume. Watch this video on exposure extortion or read The 4 Top Cybersecurity Threats of 2022 to see more dark web extortion sites.
Digging Into the Dark Web Trends
Let’s look at what is new and exciting on the dark web.
- The dark web has matured and offers shopping experience similar to the clear web. As cybercrime has matured, everything from the dark web marketplaces to cybercriminal extortion sites look like regular businesses with customer service, marketing, seller and product reviews, special discount offers, complaint resolution forms, and more.
- Dark web security is frequently stronger than clear web security. Many marketplaces use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), multiple signature verification, PGP security signing keys, anti-bot security, and more. You can now find dark web consolidated rating services that compile customer ratings from across multiple marketplaces to provide customers with a guide to the most “reputable” sources. (Yes, we appreciate the irony!) These services and most marketplaces use a seller’s PGP signing keys to verify that suppliers and communications are legitimate. These are also used to rank merchants similar to the “Power Sellers” on eBay. There are also dark web escrow services that hold the money until services or products are delivered.
- Many dark web marketplaces are moving away from Bitcoin and requesting Monero. Monero is harder to trace and is rapidly evolving as the preferred payment method for ransomware, extortion, and other illegal activities. With the US crackdown on cybercrime, this is one way some criminal groups are increasing security.
How Can you Keep Your Information Off the Dark Web?
The key is to prevent your information from being stolen in the first place. Most of the time you can’t control data disclosures because organizations that have your information get hacked. However, there are three basic cybersecurity strategies you can use to reduce the risk of hackers acquiring and effectively using your information:
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). Instead of relying on one form of authentication, MFA combines multiple methods to reduce the risk of an attack. A password may be stolen, but if the user is additionally required to confirm a login request via an app, text, or YubiKey, then this adds an extra layer of defense. See this tip sheet on passwordsand authentication for more details.
- Don’t reuse passwords. Attackers use stolen passwords to conduct credential stuffing attacks, in which they “stuff” credentials into the login forms of many different sites. Since many people re-use the same password for different sites, often the password for one service will work on another. On the dark web, attackers can buy lists of stolen LinkedIn passwords and then use automated tools to try these passwords in popular ecommerce, banking, email hosting, and other services. Attackers may also use stolen passwords to gain access to an organization’s environment so they can conduct more advanced attacks, such as ransomware, and hold the whole organization hostage.
- Check for vulnerabilities. During the past year, hackers have ramped up their vulnerability exploitation capabilities, routinely scanning the Internet for software that is outdated or missing patches, and exploiting it to install ransomware, steal data and more (Log4j, anyone?). Reduce your risks by conducting regular vulnerability scans using an effective tool.
- Conduct Regular Phishing Training and Simulations. Criminals often leverage stolen information in their scams. Make sure that your staff are prepared to recognize and resist attacks, even when criminals are armed with powerful information. Read this blog for phishing prevention tips.
We hope you now have a better understanding of how the dark web works, what to watch out for, and how to protect your organization. For all that the dark web has matured and may look more like the clear web, the dark web is still like the wild west of old—criminals can be anywhere and the rule of law has a very limited reach. If you decide to visit the dark web, do so carefully.
