How to Prevent Cyber Attacks – Including Escalating Nation State-Sponsored Attacks

Let’s dive into the details of the current nation state-sponsored attacks, look at the data on cyber espionage, and review some strategies for minimizing your organization’s risks.
The US Strengthens Its Response to Foreign Nation State-Sponsored Attacks
Four Chinese nationals have been indicted by the US for cyber espionage and are accused of hacking dozens of organizations from 2011 – 2018. These individuals are alleged to have attacked a wide range of targets – from defense contractors to schools – while searching for trade secrets and extortion opportunities. The US Department of Justice (DOJ) further alleges, “The defendants and their Hainan State Security Department (HSSD) conspirators sought to obfuscate the Chinese government’s role in such theft by establishing a front company, Hainan Xiandun Technology Development Co., Ltd.”
Acting U.S. Attorney Randy Grossman for the Southern District of California shared a bold statement,
“This indictment alleges a worldwide hacking and economic espionage campaign led by the government of China. The defendants include foreign intelligence officials who orchestrated the alleged offenses, and the indictment demonstrates how China’s government made a deliberate choice to cheat and steal instead of innovate. These offenses threaten our economy and national security, and this prosecution reflects the Department of Justice’s commitment and ability to hold individuals and nations accountable for stealing the ideas and intellectual achievements of our nation’s best and brightest people.”
China is not alone. There has been open speculation that numerous cyber attacks have also been perpetrated by state-sponsored Russian hackers. In fact, US agencies warned that the Foreign Intelligence Service of Russia, frequently referred to as SVR, has exploited multiple vulnerabilities, including the recent Microsoft Exchange Server security gap. In addition, the US formally attributed the SolarWinds hack to the SVR and announced sanctions against Russia for the SolarWinds attack and other activities. In today’s digital world, these attacks will not be going away soon. Organizations need to focus on how to prevent cyber attacks from both foreign and domestic hackers.
Which Organizations Could Be Targets?
The recent information from the DOJ means we should all be worried. Nation state-sponsored attacks are not only for espionage, but also for extortion. These attackers are well-funded and have a multitude of tools at their disposal. The 2021 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (VDBIR) data shows that while the numbers vary widely over the last few years, espionage is the motive in fewer than one-third of the data breaches reported to VDBIR since 2016.
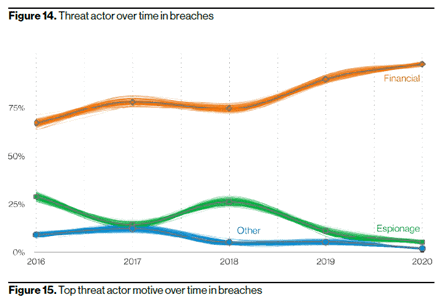
Source: 2021 VDBIR
However, as we reviewed earlier in the article, nation state-sponsored attacks have also recently included financially motivated attacks. The vast majority of data breaches are based on financially motivated attacks. This means any organizations could be a target.
How to Prevent Cyber Attacks
While cybersecurity is complex and requires the integration of many different technologies, processes, defense strategies and policies, let’s look at some of the top causes of cyber attacks as well as some prevention strategies. According to the 2021 VDBIR, the top two causes of data breaches were social engineering attacks (phishing, vishing, credential theft, etc.) and basic web application attacks. Combined, these two attack categories caused more than half of the data breaches last year. Let’s look at some strategies that can reduce your risks in these top two high-risk categories.
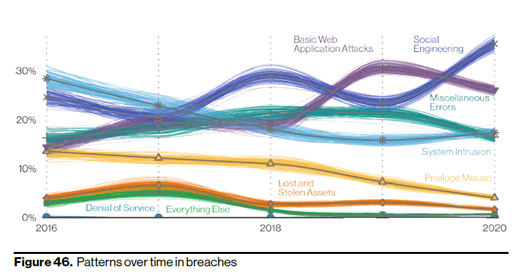
Source: 2021 VDBIR
Phishing is by far the most popular tactic for a social engineering attack. Hackers use email, phone (vishing) and even text phishing attacks to try to get users to click a link to a malicious website, download an infected file, or provide valuable information. With roughly 80% of social engineering incidents attributed to phishing, reducing your risks of “getting phished” tops our list of how to prevent cyber attacks.
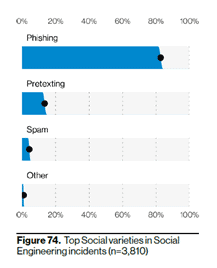
Source: 2021 VDBIR
How to Prevent Social Engineering Attacks
When it comes to preventing social engineering attacks, you need more than just technology. Everyone from employees to executives plays a role. Reduce your risks by implementing these strategies:
- User training: Train your entire organization on general cybersecurity awareness. They are your best first line of defense for phishing scams. Ensure your team always checks the email or text source, then stops and thinks about security before they click a link or download a document. This can prevent the vast majority of phishing attacks! Read our blog on what should be included in your social engineering prevention training.
- Technical phishing controls: Ensure your organization is employing technical phishing controls that will help reduce your risk. Read this article for recommendations.
- Pretexting or spear phishing awareness: Pretexting is listed as the second most popular social engineering attack in the 2021 VDBIR. Pretexting is when a hacker provides a false a story or creates a “pretext” to why you should give them information. For example, a hacker could pretend to be part of your IT team (using email or a phone call) and tell you that your email may have been hacked and they need your current password to confirm the attack. Another classic tactic is for hackers to pretend they are an executive in your organization and ask you for files or valuable information. Pretexting is largely the same as spear phishing.
- Strong passwords and multifactor authentication: We talk about these in almost every blog. These are simple, inexpensive steps that should be part of every organization’s cybersecurity defense strategy. Read this blog to find out more about multifactor authentication and read our password tip sheet for more information.
Combatting Web Application Breaches
Combating web application breaches is a little more complex. Even with safe web apps, good configuration, and strong policies, zero-day exploits are still a risk. Our top recommendations for reducing risks are:
- Web application assessments: These assessments examine the risks of each web application from intrinsic app security to your configuration settings. Whether you get an assessment or do it yourself, your IT team needs to know what components are used in your web apps and be vigilant about patching/updating your apps. In addition, they will also wish to monitor your app providers for any issues (the recent Kaseya breach is a concerning example) so you can manage your 3rd party vendor risks.
- Logging and monitoring: Another critical aspect to consider is logging/monitoring. Ensure your organization is appropriately logging your web app events (and events throughout your environment) and that you have an appropriate retention policy. Strong logging and monitoring are foundational elements of cybersecurity and a prerequisite to one of the most helpful proactive prevention strategies for almost all attack vectors – threat hunting. For more information on logging and monitoring benefits and best practices, watch our on-demand webinar.
- Proactive Threat Hunting: It’s impossible to stop every intrusion. But regular proactive threat hunting can help your organization spot threats and find hackers that are already in your system before they deploy ransomware or gather extensive data. Many hackers dwell for weeks or months in your system while escalating privileges and gathering information. Proactive threat hunting is one of the best ways to discover and stop hackers that have breached your network. For more information, read this proactive threat hunting blog.
A strong cybersecurity posture that protects your organization from cyber attacks requires a holistic multifaceted security program. However, understanding the risks and motivations of attackers, as well as implementing these tips for how to prevent cyber attacks, can go a long way to reducing your risks.
Please contact us if would like help with cybersecurity testing, training, incident response or advisory and consulting services.
